RealSmileNet: A Deep End-To-End Network for Spontaneous and Posed Smile Recognition
Yan Yang (Australian National University)*, Md Zakir Hossain (The Australian National University ), Tom Gedeon (The Australian National University), Shafin Rahman (North South University)
Keywords: Face, Pose, Action, and Gesture
Abstract:
Smiles play a vital role in the understanding of social interactions within different communities, and reveals the physical state of mind of people in both real and deceptive ways. Several methods have been proposed to recognize spontaneous and posed smiles. All follow a feature-engineering based pipeline requiring costly pre-processing steps such as manual annotation of face landmarks, tracking, segmentation of smile phases, and hand-crafted features. The resulting computation is expensive, and strongly dependent on pre-processing steps. We investigate an end-to-end deep learning model to address these problems, the first end-to-end model for spontaneous and posed smile recognition. Our fully automated model is fast and learns the feature extraction processes by training a series of convolution and ConvLSTM layer from scratch. Our experiments on four datasets demonstrate the robustness and generalization of the proposed model by achieving state-of-the-art performances.
SlidesLive
Similar Papers
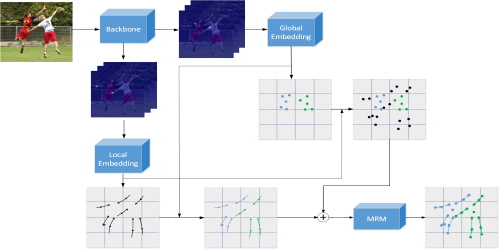
A Global to Local Double Embedding Method for Multi-person Pose Estimation
Yiming Xu (UESTC)*, Jiaxin Li (Beijing Institute of Technology), Yan Ding (Beijing Institute of Technology), Hua-Liang Wei (University of Sheffield)
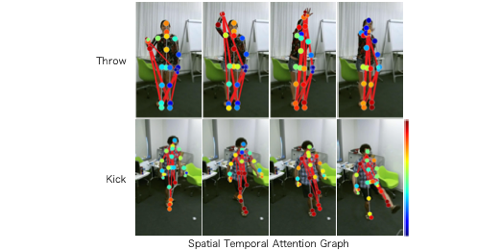
Spatial Temporal Attention Graph Convolutional Networks with Mechanics-Stream for Skeleton-based Action Recognition
Katsutoshi Shiraki (Chubu University)*, Tsubasa Hirakawa (Chubu University), Takayoshi Yamashita (Chubu University), Hironobu Fujiyoshi (Chubu University)
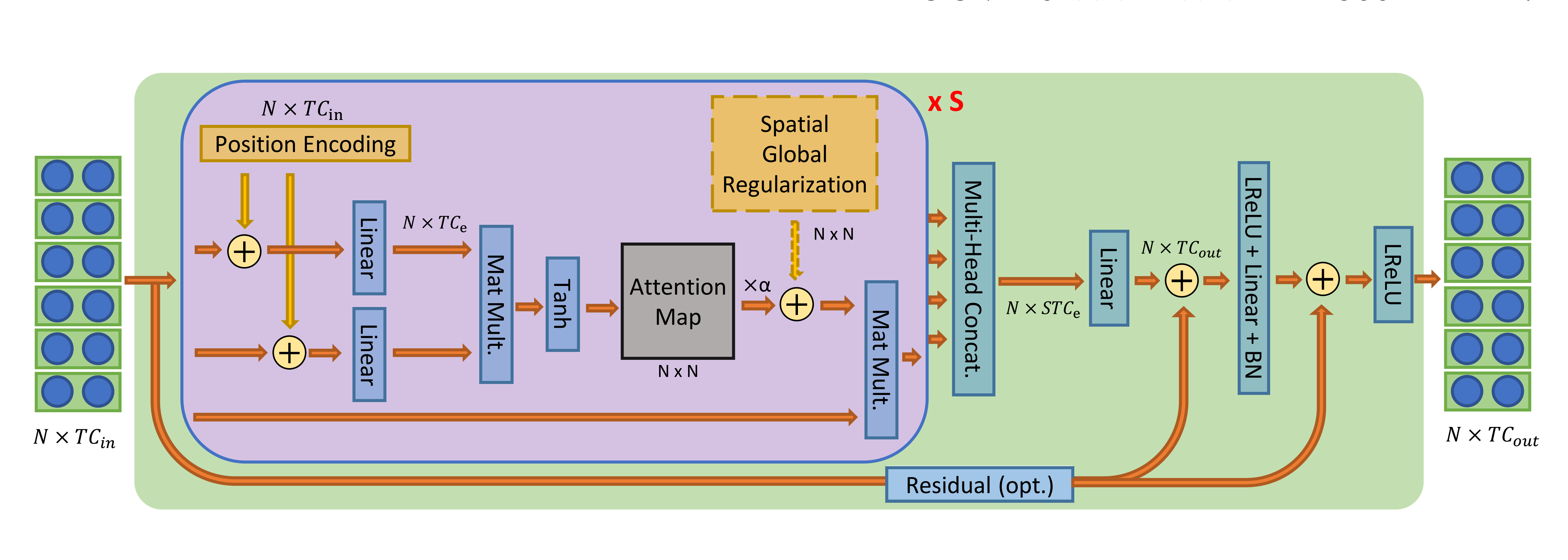
Decoupled Spatial-Temporal Attention Network for Skeleton-Based Action-Gesture Recognition
Lei Shi (Institute of Automation_�Chinese Academy of Sciences )*, Yifan Zhang (Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences), Jian Cheng ("Chinese Academy of Sciences, China"), Hanqing Lu (NLPR, Institute of Automation, CAS)