Depth-Adapted CNN for RGB-D cameras
Zongwei WU (Univ. Bourgogne Franche-Comte, France)*, Guillaume Allibert (Université Côte d’Azur, CNRS, I3S, France ), Christophe Stolz (Univ. Bourgogne Franche-Comte, France), Cedric Demonceaux (Univ. Bourgogne Franche-Comte, France)
Keywords: RGBD and Depth Image Processing
Abstract:
Conventional 2D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) extract features from an input image by applying linear filters. These filters compute the spatial coherence by weighting the photometric information on a fixed neighborhood without taking into account the geometric information. We tackle the problem of improving the classical RGB CNN methods by using the depth information provided by the RGB-D cameras. State-of-the-art approaches use depth as an additional channel or image (HHA) or pass from 2D CNN to 3D CNN. This paper proposes a novel and generic procedure to articulate both photometric and geometric information in CNN architecture. The depth data is represented as a 2D offset to adapt spatial sampling locations. The new model presented is invariant to scale and rotation around X and Y axis of the camera coordinate system. Moreover, when depth data is constant, our model is equivalent to a regular CNN. Experiments of benchmarks validate the effectiveness of our model.
SlidesLive
Similar Papers
Leveraging Tacit Information Embedded in CNN Layers for Visual Tracking
Kourosh Meshgi (RIKEN AIP)*, Maryam Sadat Mirzaei (Riken AIP / Kyoto University), Shigeyuki Oba (Kyoto University)
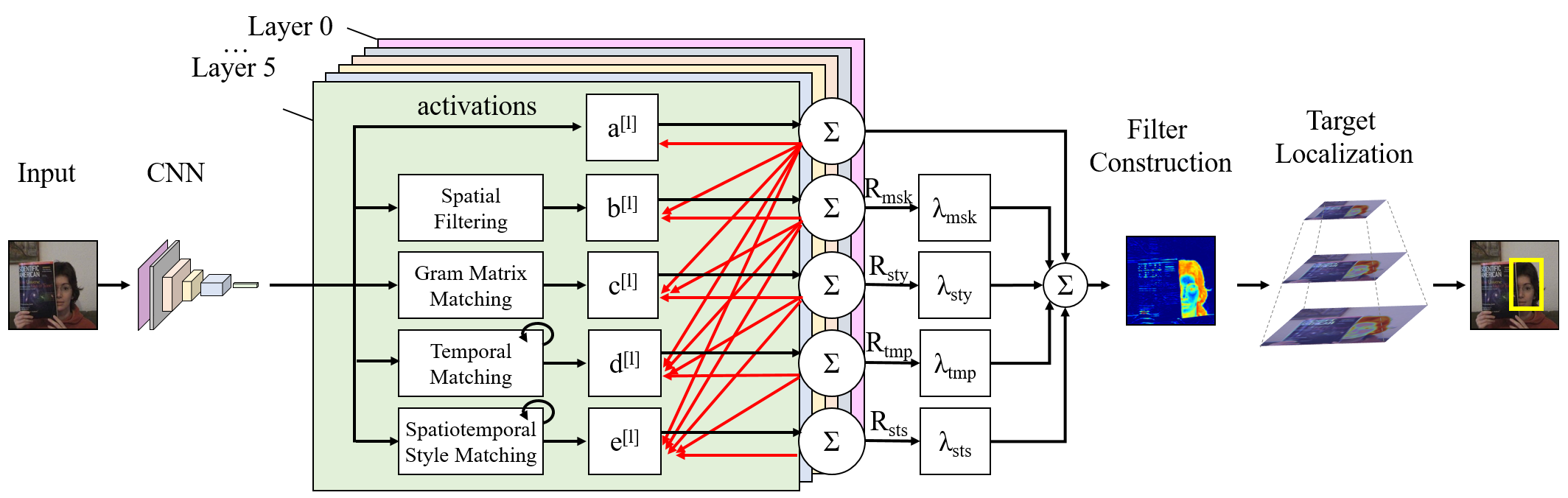
Frequency Attention Network: Blind Noise Removal for Real Images
Hongcheng Mo (Shanghai Jiao Tong University), Jianfei Jiang (Shanghai Jiao Tong University), Qin Wang (Shanghai Jiao Tong University)*, Dong Yin (Fullhan), Pengyu Dong (Fullhan), Jingjun Tian (Fullhan)
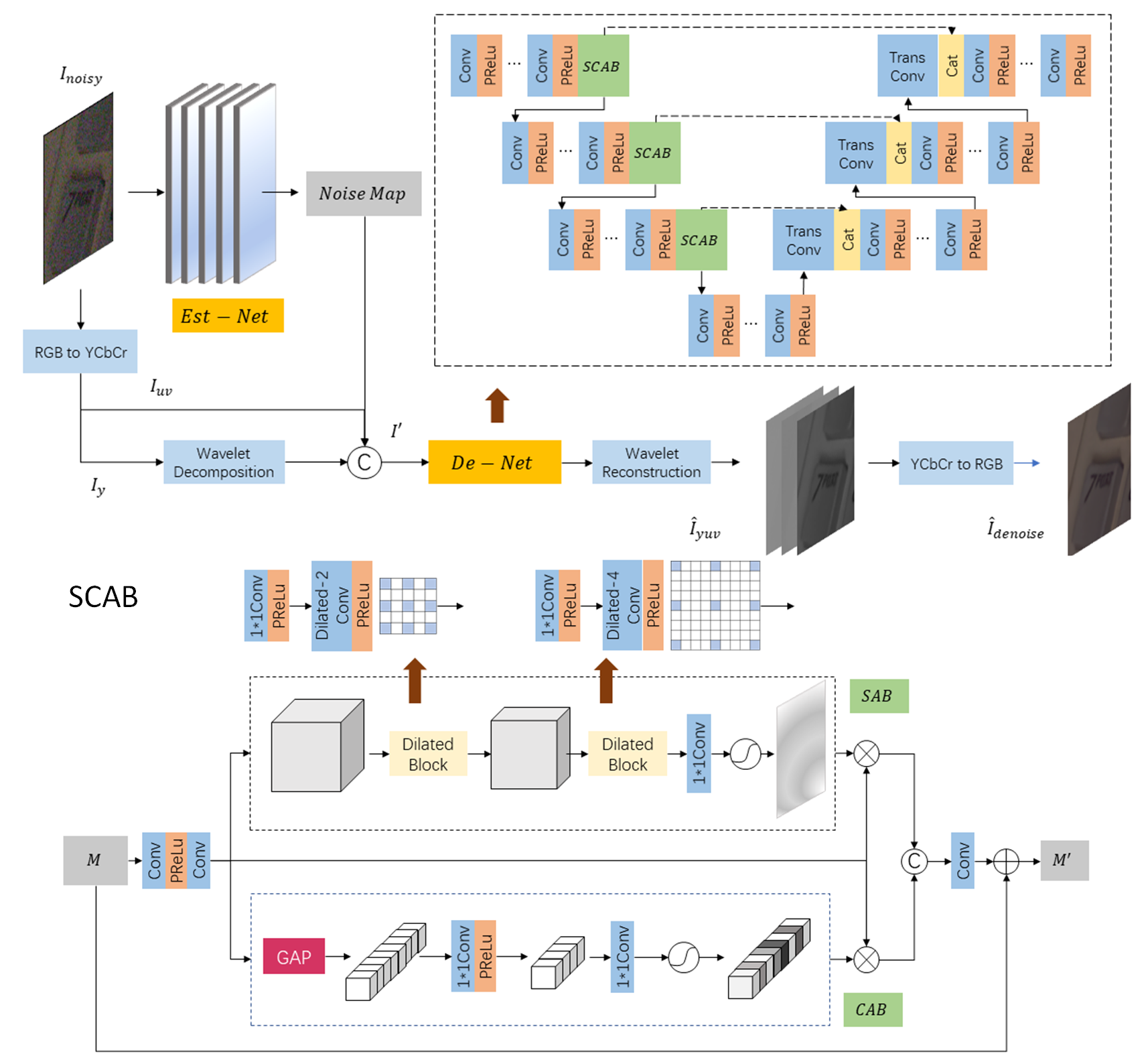
Color Enhancement using Global Parameters and Local Features Learning
Enyu Liu (Tencent)*, Songnan Li (Tencent), Shan Liu (Tencent America)