Regularizing Meta-Learning via Gradient Dropout
Hung-Yu Tseng (University of California, Merced)*, Yi-Wen Chen (University of California, Merced), Yi-Hsuan Tsai (NEC Labs America), Sifei Liu (NVIDIA), Yen-Yu Lin (National Chiao Tung University), Ming-Hsuan Yang (University of California at Merced)
Keywords: Deep Learning for Computer Vision
Abstract:
With the growing attention on learning-to-learn new tasks using only a few examples, meta-learning has been widely used in numerous problems such as few-shot classification, reinforcement learning, and domain generalization. However, meta-learning models are prone to overfitting when there are no sufficient training tasks for the meta-learners to generalize. Although existing approaches such as Dropout are widely used to address the overfitting problem, these methods are typically designed for regularizing models of a single task in supervised training.In this paper, we introduce a simple yet effective method to alleviate the risk of overfitting for gradient-based meta-learning. Specifically, during the gradient-based adaptation stage, we randomly drop the gradient in the inner-loop optimization of each parameter in deep neural networks, such that the augmented gradients improve generalization to new tasks. We present a general form of the proposed gradient dropout regularization and show that this term can be sampled from either the Bernoulli or Gaussian distribution. To validate the proposed method, we conduct extensive experiments and analysis on numerous computer vision tasks, demonstrating that the gradient dropout regularization mitigates the overfitting problem and improves the performance upon various gradient-based meta-learning frameworks.
SlidesLive
Similar Papers
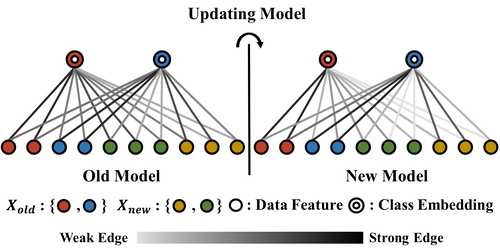
Large-Scale Cross-Domain Few-Shot Learning
Jiechao Guan (Renmin University of China), Manli Zhang (Renmin University of China), Zhiwu Lu (Renmin University of China)*
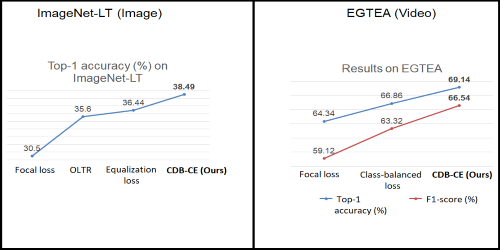
Class-Wise Difficulty-Balanced Loss for Solving Class-Imbalance
Saptarshi Sinha (Hitachi CRL)*, Hiroki Ohashi (Hitachi Ltd), Katsuyuki Nakamura (Hitachi Ltd.)
Class-incremental Learning with Rectified Feature-Graph Preservation
Cheng-Hsun Lei (National Chiao Tung University), Yi-Hsin Chen (National Chiao Tung University), Wen-Hsiao Peng (National Chiao Tung University), Wei-Chen Chiu (National Chiao Tung University)*