FAN: Feature Adaptation Network for Surveillance Face Recognition and Normalization
Xi Yin (Microsoft Cloud & AI)*, Ying Tai (Tencent YouTu), Yuge Huang (Tencent YouTu), Xiaoming Liu (Michigan State University)
Keywords: Low-level Vision, Image Processing
Abstract:
This paper studies face recognition (FR) and normalization in surveillance imagery. Surveillance FR is a challenging problem that has great values in law enforcement. Despite recent progress in conventional FR, less effort has been devoted to surveillance FR. To bridge this gap, we propose a Feature Adaptation Network (FAN) to jointly perform surveillance FR and normalization. Our face normalization mainly acts on the aspect of image resolution, closely related to face super-resolution. However, previous face super-resolution methods require paired training data with pixel-to-pixel correspondence, which is typically unavailable between real-world low-resolution and high-resolution faces. FAN can leverage both paired and unpaired data as we disentangle the features into identity and non-identity components and adapt the distribution of the identity features, which breaks the limit of current face super-resolution methods. We further propose a random scale augmentation scheme to learn resolution robust identity features, with advantages over previous fixed scale augmentation. Extensive experiments on LFW, WIDER FACE, QUML-SurvFace and SCface datasets have shown the effectiveness of our method on surveillance FR and normalization.
SlidesLive
Similar Papers
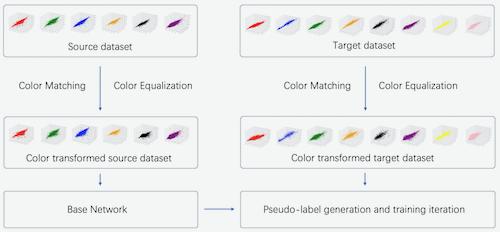
Second-order Camera-aware Color Transformation for Cross-domain Person Re-identification
Wangmeng Xiang (The Hong Kong Polytechnic University), Hongwei Yong (The Hong Kong Polytechnic University), Jianqiang Huang (Damo Academy, Alibaba Group), Xian-Sheng Hua (Alibaba Group), Lei Zhang ("Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, China")*
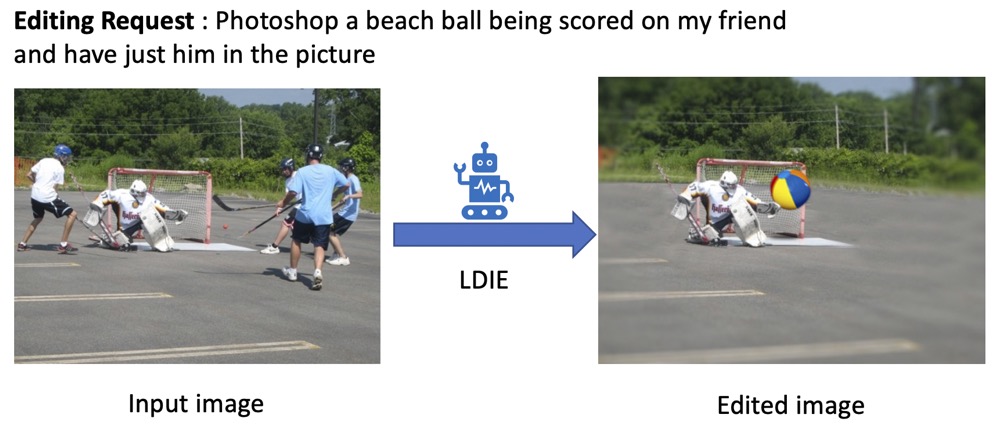
A Benchmark and Baseline for Language-Driven Image Editing
Jing Shi (University of Rochester)*, Ning Xu (Adobe Research), Trung Bui (Adobe Research), Franck Dernoncourt (Adobe Research), Zheng Wen (DeepMind), Chenliang Xu (University of Rochester)
Synthetic-to-real domain adaptation for lane detection
Noa Garnett (GM), Roy Uziel (Ben-Gurion University), Netalee Efrat (General Motors), Dan Levi (General Motors)*
