Utilizing Transfer Learning and a Customized Loss Function for Optic Disc Segmentation from Retinal Images
Abdullah Sarhan (University of Calgary)*, Ali Al-Khaz'Aly (University of Calgary), Adam Gorner (University of Calgary), Andrew Swift (University of Calgary), Jon Rokne (University of Calgary), Reda Alhajj (University of Calgary), Andrew Crichton (University of Calgary)
Keywords: Segmentation and Grouping
Abstract:
Accurate segmentation of the optic disc from a retinal image is vital to extracting retinal features that may be highly correlated with retinal conditions such as glaucoma. In this paper, we propose a deep-learning based approach capable of segmenting the optic disc given a high-precision retinal fundus image. Our approach utilizes a UNET-based model with a VGG16 encoder trained on the ImageNet dataset. This study can be distinguished from other studies in the customization made for the VGG16 model, the diversity of the datasets adopted, the duration of disc segmentation, the loss function utilized, and the number of parameters required to train our model. Our approach was tested on seven publicly available datasets augmented by a dataset from a private clinic that was annotated by two Doctors of Optometry through a web portal built for this purpose. We achieved an accuracy of 99.78\% and a Dice coefficient of 94.73\% for a disc segmentation from a retinal image in 0.03 seconds. The results obtained from comprehensive experiments demonstrate the robustness of our approach to disc segmentation of retinal images obtained from different sources.
SlidesLive
Similar Papers
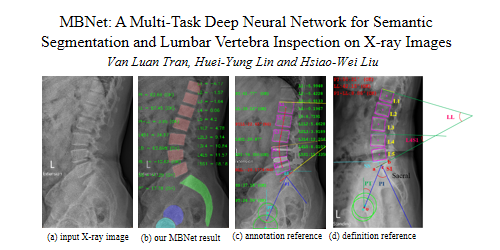
MBNet: A Multi-Task Deep Neural Network for Semantic Segmentation and Lumbar Vertebra Inspection on X-ray Images
Van Luan Tran (National Chung Cheng University)*, Huei-Yung Lin (National Chung Cheng University), Hsiao-Wei Liu (Industrial Technology Research Institute (ITRI))
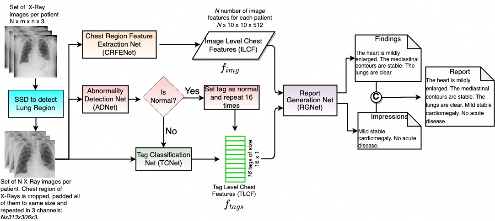
Hierarchical X-Ray Report Generation via Pathology tags and Multi Head Attention
Preethi Srinivasan (IIT Mandi), Daksh Thapar (Indian Institute of Technology, Mandi)*, Arnav Bhavsar (IIT Mandi), Aditya Nigam (IIT mandi)
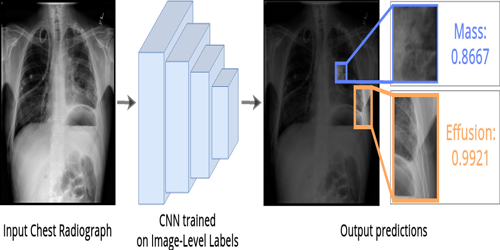
Self-Guided Multiple Instance Learning forWeakly Supervised Thoracic DiseaseClassification and Localizationin Chest Radiographs
Constantin Seibold (Karlsruhe Institute of Technology)*, Jens Kleesiek (German Cancer Research Center), Heinz-Peter Schlemmer (German Cancer Research Center), Rainer Stiefelhagen (Karlsruhe Institute of Technology)