Abstract:
Many computer vision applications need to recover structure from imperfect measurements of the real world. The task is often solved by robustly fitting a geometric model onto noisy and outlier-contaminated data. However, recent theoretical analyses indicate that many commonly used formulations of robust fitting in computer vision are not amenable to tractable solution and approximation. In this paper, we explore the usage of quantum computers for robust fitting. To do so, we examine and establish the practical usefulness of a robust fitting formulation inspired by the analysis of monotone Boolean functions. We then investigate a quantum algorithm to solve the formulation and analyse the computational speed-up possible over the classical algorithm. Our work thus proposes one of the first quantum treatments of robust fitting for computer vision.
SlidesLive
Similar Papers
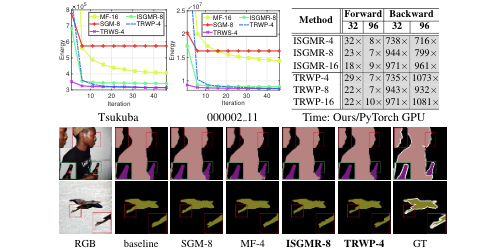
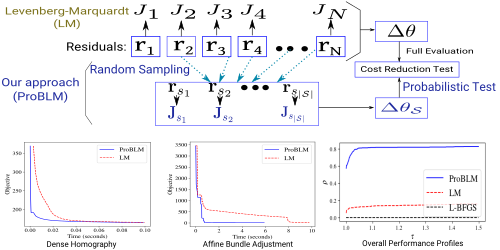
Progressive Batching for Efficient Non-linear Least Squares
Huu Le (Chalmers University of Technology)*, Christopher Zach (Chalmers University), Edward Rosten (Snap Inc.), Oliver J. Woodford (Snap Inc)
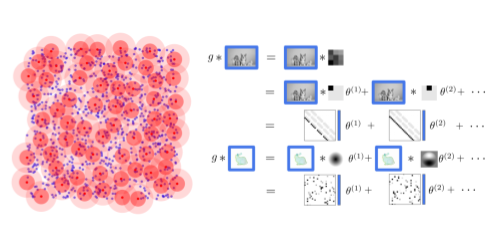
Sparse Convolutions on Continuous Domains for Point Cloud and Event Stream Networks
Dominic Jack (Queensland University of Technology)*, Frederic Maire (Queensland University of Technology), SIMON DENMAN (Queensland University of Technology, Australia), Anders Eriksson (University of Queensland )
Fast and Differentiable Message Passing on Pairwise Markov Random Fields
Zhiwei Xu (Australian National University)*, Thalaiyasingam Ajanthan (ANU), RICHARD HARTLEY (Australian National University, Australia)