Pose Correction Algorithm for Relative Frames between Keyframes in SLAM
Youngseok Jang (Seoul National University)*, Hojoon Shin (Seoul National University), H. Jin Kim (Seoul National University)
Keywords: Applications of Computer Vision, Vision for X
Abstract:
With the dominance of keyframe-based SLAM in the field of robotics, the relative frame poses between keyframes have typically been sacrificed for a faster algorithm to achieve online applications. However, those approaches can become insufficient for applications that may require refined poses of all frames, not just keyframes which are relatively sparse compared to all input frames. This paper proposes a novel algorithm to correct the relative frames between keyframes after the keyframes have been updated by a back-end optimization process. The correction model is derived using conservation of the measurement constraint between landmarks and the robot pose. The proposed algorithm is designed to be easily integrable to existing keyframe-based SLAM systems while exhibiting robust and accurate performance superior to existing interpolation methods. The algorithm also requires low computational resources and hence has a minimal burden on the whole SLAM pipeline. We provide the evaluation of the proposed pose correction algorithm in comparison to existing interpolation methods in various vector spaces, and our method has demonstrated excellent accuracy in both KITTI and EuRoC datasets.
SlidesLive
Similar Papers
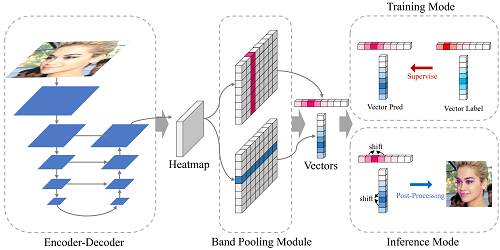
Gaussian Vector: An Efficient Solution for Facial Landmark Detection
Yilin Xiong (Central South University)*, Zijian Zhou (Horizon), yuhao dou (Horizon), ZHIZHONG SU (Horizon Robotics)
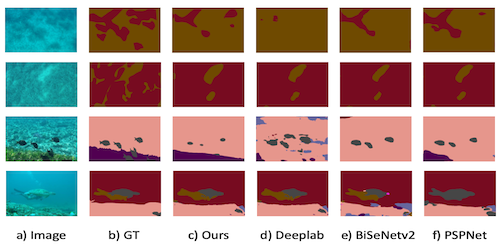
Compact and Fast Underwater Segmentation Network for Autonomous Underwater Vehicles
Jiangtao Wang (Loughborough University), Baihua Li (Loughborough University)*, Yang Zhou (Loughborough University), Emanuele Rocco (Witted Srl), Qinggang Meng (Computer Science Department Loughborough University)
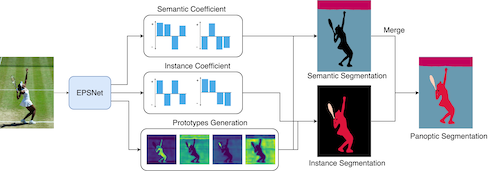
EPSNet: Efficient Panoptic Segmentation Network with Cross-layer Attention Fusion
Chia-Yuan Chang (National Taiwan University)*, Shuo-En Chang (National Taiwan University), Pei-Yung Hsiao (National University of Kaohsiung), Li-Chen Fu (National Taiwan University)