In Defense of LSTMs for Addressing Multiple Instance Learning Problems
Kaili Wang (KU Leuven, UAntwerpen)*, Jose Oramas (UAntwerp, imec-IDLab), Tinne Tuytelaars (KU Leuven)
Keywords: Applications of Computer Vision, Vision for X
Abstract:
LSTMs have a proven track record in analyzing sequential data. But what about unordered instance bags, as found under a Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) setting? While not often used for this, we show LSTMs excell under this setting too. In addition, we show thatLSTMs are capable of indirectly capturing instance-level information us-ing only bag-level annotations. Thus, they can be used to learn instance-level models in a weakly supervised manner. Our empirical evaluation on both simplified (MNIST) and realistic (Lookbook and Histopathology) datasets shows that LSTMs are competitive with or even surpass state-of-the-art methods specially designed for handling specific MIL problems. Moreover, we show that their performance on instance-level prediction is close to that of fully-supervised methods
SlidesLive
Similar Papers
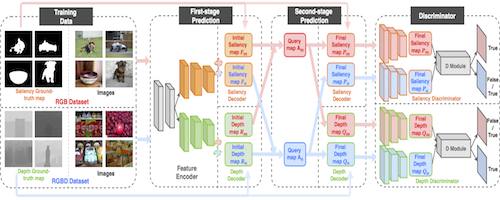
Synergistic Saliency and Depth Prediction for RGB-D Saliency Detection
Yue Wang (Dalian University of Technology), Yuke Li (UC Berkeley), James H. Elder (York University), Runmin Wu (Dalian University of Technology ), Huchuan Lu (Dalian University of Technology)*, Lu Zhang (Dalian University of Technology)
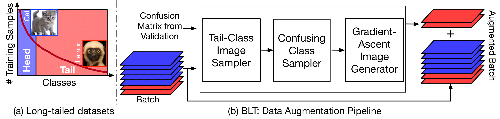
BLT: Balancing Long-Tailed Datasets with Adversarially-Perturbed Images
Jedrzej Kozerawski (UC Santa Barbara), Victor Fragoso (Microsoft)*, Nikolaos Karianakis (Microsoft), Gaurav Mittal (Microsoft), Matthew Turk (TTIC), Mei Chen (Microsoft)
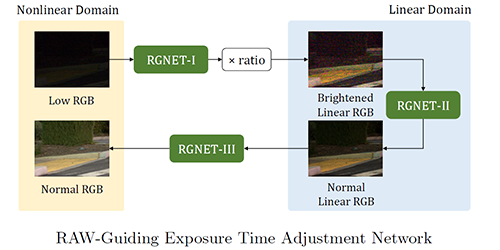
Raw-Guided Enhancing Reprocess of Low-Light Image via Deep Exposure Adjustment
Haofeng Huang (Peking University)*, Wenhan Yang (Peking University), Yueyu Hu (Peking University), Jiaying Liu (Peking University)